 Accurate knowledge of the frequency distribution of strong surface wind is of major relevance for insurance related risks in Europe. The risk of wind it a kind of not so a popular risk that people are very afraid. As financial losses due to weather extremes escalate, in the development of information related with of wind storm over Europe. The series of number of strong winds shows that in the last 40 years is accompanied by an increase in year-to-year of this phenomenon.
Accurate knowledge of the frequency distribution of strong surface wind is of major relevance for insurance related risks in Europe. The risk of wind it a kind of not so a popular risk that people are very afraid. As financial losses due to weather extremes escalate, in the development of information related with of wind storm over Europe. The series of number of strong winds shows that in the last 40 years is accompanied by an increase in year-to-year of this phenomenon.
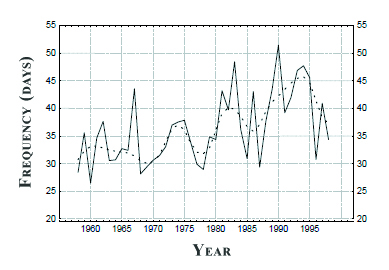
The series of number of strong winds (MeteoSchweiz n°216).
Some weeks ago I experience very windy afternoon in Toruń (city in Poland), a big tree felt down in front of the Department of Nicolaus Copernicus University and crashing into a car, the phenomenon shows how dangerous and extreme strong winds can be.
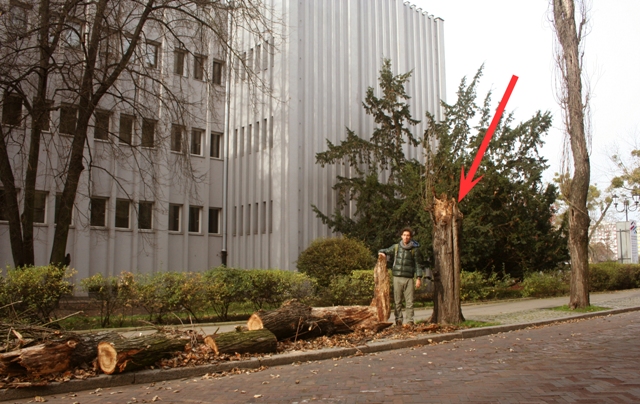

Results of a very windy afternoon in Toruń, Poland (Photo: Ewa Zukrowska).
After some weeks the North Europe had suffered strong winds. The wind speeds reached more than 150 kph leaving a trail of damage across Europe. The wind brought down trees, blew roofs off houses and turned over trucks, leaving at least 600.000 people without electricity. As consequence of strong winds England, Germany, Denmark, Poland, Sweden and Netherland had some trees that had felt down, cut roads and railways, causing chaos. In a neighbour of London, the city cut the electricity that created a shot circuit followed by a gas explosion.

Evolution of the wind storm in Europe in octuber 2013 (MetOffice)
Climate change has promoted a wide study of the potential impacts of the enhanced green-house effect on the frequency of violent winds. The analysis of extreme winds follows two main different points of view: spatially distributed and generalized view. The magnitude and frequency of extreme wind speed is of fundamental importance for many safety of the society with more risks.
