Our thinkinazul project Molico-CV presented four works at the XII Jornadas de Geomorfologia Litoral held in Valencia (Spain) from September 25 to 27, 2024.
- Morphometric analysis of the Alicante coast.
- The Ifach Rock and the coast between Calpe and Moraira.
- Side Scan Sonar in Morro de Toix (Calpe).
- The notch in Morro de Toix (Calpe).

Works presented to the XII Jornadas de Geomorfología Litoral:
- Alcántara Carrió, J., Tent Manclús, J. E., Bonomo, D., Fontán Bouzas, A., Portz, L. y Manzolli, R. (2024): High-resolution morphometric analysis of the rocky coast of the Prebetic System (southeast Iberian Peninsula). In: Palomar Vazquez, J. y Pardo Pascual, J. (Eds.). GEOLIT24 – Libro de Actas – XII Jornadas de Geomorfología Litoral. 25-27 de septiembre de 2024. Valencia. 214-220. https://doi.org/10.4995/GEOLIT24.2024.18736
- Alcántara Carrió, J., Tent Manclús, J. E., Bonomo, D., Fontán Bouzas, A., Portz, L. y Manzolli, R. (2024): The Pleistocene double tombolo of Calpe and the submerged fault scarps between Moraria Point and Ifach Rock (southeast Iberian Peninsula). In: Palomar Vazquez, J. y Pardo Pascual, J. (Eds.). GEOLIT24 – Libro de Actas – XII Jornadas de Geomorfología Litoral. 25-27 de septiembre de 2024. Valencia. 221-227. https://doi.org/10.4995/GEOLIT24.2024.18864.
- Bonomo, D., Ronda, J. L., Benabdeloued, B. Y. N., Tent-Manclús, J. E., Salcedo-Justicia, E. M. y Alcántara-Carrió, J. (2024): Estudio con sonar de barrido lateral de la base del acantilado del Morro de Toix (Calpe, Alicante). In: Palomar Vazquez, J. y Pardo Pascual, J. (Eds.). GEOLIT24 – Libro de Actas – XII Jornadas de Geomorfología Litoral. 25-27 de septiembre de 2024. Valencia. 254-259. https://doi.org/10.4995/GEOLIT24.2024.18726.
- Tent-Manclús, J. E., Bonomo, D., Alcántara-Carrió, J. y Salcedo-Justicia, E. M. (2024): Evolución reciente del notch del acantilado marino del Morro de Toix (Alicante, SE España). In: Palomar Vazquez, J. y Pardo Pascual, J. (Eds.). GEOLIT24 – Libro de Actas – XII Jornadas de Geomorfología Litoral. 25-27 de septiembre de 2024. 318-323. Valencia. https://doi.org/10.4995/GEOLIT24.2024.18729
Tags: marine geology, USV
The 19 International Nannoplankton Association Congress took place on the coastal city of Llandudno (Wales) from September 9 until 13, 2024.
The Ceratoliths are a type of calcareous nannoplankton which allow to subdivided the Messinian and the Pliocene stages. A series of works by Carlos Lancis, José Enrique Tent-Manclús and José-Abel Flores, comparing Light Microscope and Scan Electronic Microscope image, have redefined the Messinian and Pliocene Ceratolithaceae Family and its unrevail its phylogenetic evolution.

Three works published in the Journal of Nannoplankton Research (JNR) abstract volume (here):
- Lancis, C., Tent-Manclús, J. E. y Flores, J.-A. (2024): Ceratolithaceae biostratigraphy of ODP Hole 999A, Caribbean Sea. Journal of Nannoplankton Research, 42-special: 71.
- Lancis, C., Tent-Manclús, J. E. y Flores, J.-A. (2024): Ceratolithaceae biostratigraphy of ODP Site 1237, equatorial Pacific. Journal of Nannoplankton Research, 42-special: 72.
- Lancis, C., Tent-Manclús, J. E. y Flores, J.-A. (2024): Structural developments within the Family Ceratolithaceae. Journal of Nannoplankton Research, 42-special: 73.
Tags: meetings
Our thinkinazul project Molico-CV presented three presentations at the XI Spanish Geological Congress held in Ávila (Spain) from July 1 to 6, 2024.
- A high energy event in the last 2000 years at Guardamar de Segura.
- The Seacliff of Morro de Toix (Alicante)
- The development of a homemade USV (Uncrewed Surface Vehicle). See the picture bellow.

Works presented to the XI Spanish Geological Congress:
- Benabdeloued, B. Y. N., Ronda, J. L., Tent-Manclús, J. E., Bonomo, D. y Alcántara-Carrió, J. (2024): Desarrollo de un USV para trabajos costeros. Geotemas, 20: 46.
- Bonomo, D., Tent-Manclús, J. E., Alcántara-Carrió, J., Portantiolo Manzolli, R., Jordá Guijarro, J., Arteaga Cardineau, C., Navarro Pedreño, J., Jordan, M., y Narváez, C. R. (2024): Registro de un evento de alta energía en la planicie costera de Guardamar de Segura (Alicante, SE España). Geotemas, 20: 1132-1135.
- Tent-Manclús, J. E., Bonomo, D., Alcántara-Carrió, J. y Estévez, A. (2024): Evolución reciente del acantilado marino del Morro de Toix (Alicante, SE España). Geotemas, 20: 89-92.
Tags: Alicante coast, Guardamar de Segura, USV
Last june 11th to 13th 2024 in the Universidad de Alicante facilities took place the third meeting of the of the Valencian Comunity Thinkinazul project.
The meeting was in the Alfredo Orts degrees room. Below a picture of some of the attendents.

Tags: Alicante University, Meeting
Students in the third year of the Geology Degree of the course “Geophysics and geophysical prospecting”, under the supervision of Professor José Enrique Tent Manclús, carried out practices in the University of Alicante Ducks pond to learn how to drive a ROV. The picture show some students trying to understand the ROV commands (left).

Tags: Alicante University
Last February 15th, 2023, students in the third year of the Geology Degree of the course “Geophysics and geophysical prospecting”, under the supervision of Professor José Enrique Tent Manclús, carried out practices aboard the “Rosa de Abril” boat from the Alicante harbor. The practice was show a Boomer High resolution reflexion equipment and a ROV. The picture show a student trying to understand the ROV commands.

Tags: Geology degree, Geophysics
Sediment samples of deep marine oceanic ODP boreholes from sites 999 in the Caribbean Sea and 1237 in the Eastern Pacific Ocean covering the period between 6 and 4.5 Ma have been studied with a focus on ceratolith evolution. Orthorhabdus rugosus is a nannolith with three blades (sinistral, median, and dextral) that first appeared during the Serravallian, it is not-birefringent in its stable orientation. It shows a high morphological variability time-interval at the end of the Messinian to the basal Pliocene (5.5 to 5 Ma) during which Ceratolithus (5.484 Ma) evolved. Changes occurred in the sinistral and median blades, whilst the dextral blade was reduced. Ceratolithus finifer n. comb is the first species of the evolutionary line. The nannolith stable position changed during its evolution, resulting in the older forms showing low birefringence and the younger ones moderate to high birefringence in the most stable orientation. Ceratolithus acutus, with an arrowhead shape, Ceratolithus armatus, and the morphologically distinct C. larrymayeri evolved from C. finifer with all three species showing high birefringence. The previous O. rugosus and C. finifer continued. Finally, C. armatus gives rise to C. cristatus. Ceratolithus atlanticus and C. tricorniculatus also evolved from C. finifer. All the species mentioned become extinct during the Pliocene except Ceratolithus cristatus that lives today. Detailed observations permit the analysis of the evolutionary trends of the group, possible mechanisms, patterns, and processes of speciation, and establish new criteria to define the species that, by their relative abundance and short geologic range, have permitted adjustment of biostratigraphic markers for this period.
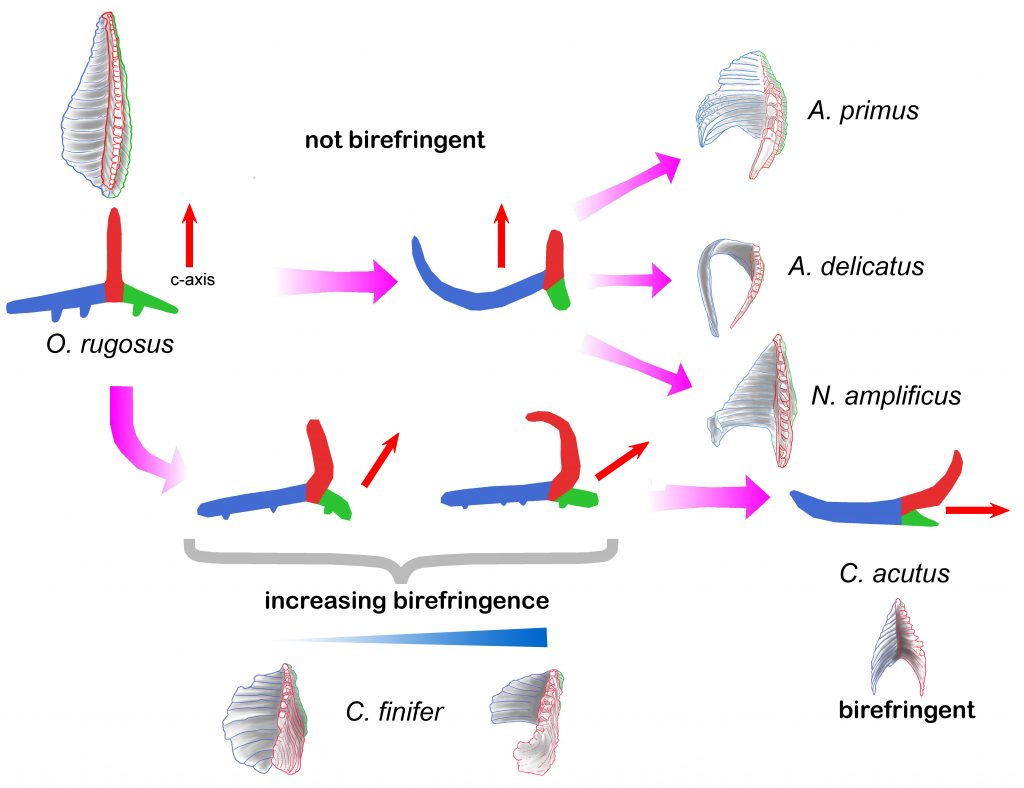
Development of birefringence in the family Ceratolithaceae. Upper part, the first variability interval when Amaurolithus primus, Amaurolithus delicatus, and Nicklithus amplificus evolved from Orthorhabdus rugosus. As the median wing (in red) does not change its orientation, remaining perpendicular to the most stable position, pointing upwards, those species do not show birefringence. The lower part shows the O. rugosus second variability interval when Ceratolithus developed. The early forms, Ceratolithus finifer, show low birefringence as the c-axis/median wing (in red) incline towards the dextral wing (in green). In the later morphotypes the c-axis/ median wing rotates, tilting the nannolith most stable position to the right, and so showing moderate to high birefringence. Finally, when the lath-end of the sinistral wing (in blue) of C. acutus rotates upwards, the nannolith most stable position tilts further to the right orienting the c-axis parallel to it, producing the high birefringence characteristic of Ceratolithus.
Cite as: Lancis, C., Tent-Manclús, J.-E., Flores, J.-A., 2024. Origin and evolution of the Neogene calcareous nannofossil Ceratolithus. Mar. Micropaleontol. 186, 102310. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marmicro.2023.102310
Tags: calcareous nannofossil evolution, ceratolithus, ODP Hole 999A, ODP Site 1237, Orthorhabdus
This year the students of the third course of Marine sciences of the Alicante University visit the Mesa de Rodan, Cabo de Gata, and Sorbas basin on November 2nd and 3th of 2023.

The picture show the student visiting the Sorbas gypsum karst (Almeria).
The professors of the subject were Antonio Estévez, Manuel Martín-Martín, David Bonomo, and José Enrique Tent-Manclús.
Tags: Almeria, gypsum karst, Sorbas


Award for the best article in the field of marine technology and renewable energy sponsored by Nautilus Oceanica at the Martech 2023 congress, Tenth international workshop on marine technology, Jaume I University, Castellón de la Plana. For the article entitled: “Low cost USV development to study spring ponds” by Ronda, J. L., Benabdeloued, B. Y. N. and Tent-Manclús, J. E. belonging to the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences and the Seismic Network of the Valencian Community (SISCOVA).

Award concession, from left to right: Alejandro Palmeriro Nautilus Oceanica representative, Raúl Marín Prades chairman of the organizing committee, Pedro José Sanz Valero del Irtesu, José Enrique Tent Manclús, Nassim Benabdeloued, Juan Leandro Ronda.
The article deals with the development of a USV (Unmanned Surface Vehicle) a surface unmanned ship for the study of springs. It is a small remote-controlled vehicle with a control post, from where it is manned. It has two cameras, one underwater and one frontal, which transmit real-time GPS location, also in real time, and bathymetry probe sensors and side-scan Sonar.

The USV and the authors of the work. From left to right: Juan Leandro Ronda, José Enrique Tent-Manclús y Nassim Benabdeloued
The authors with the USV team.


Tags: USV
The project will study changes in the coast-line, coastal risk and coastal aquifers, an its logo is:

The leadership of the project is carried out by researches of the MIES is a Multidisciplinary Research Institute for Environmental Studies “Ramón Margalef” (Instituto Multidisciplinario para el estudio del Medio “Ramon Margalef”, IMEM in Spanish) of the Alicante University and integrate researches of 10 universities and research institutions.

The EU funded ThinkInAzul programme supported by MCIN (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación) with funding from European Union NextGenerationEU (PRTR-C17.I1) and by Generalitat Valenciana
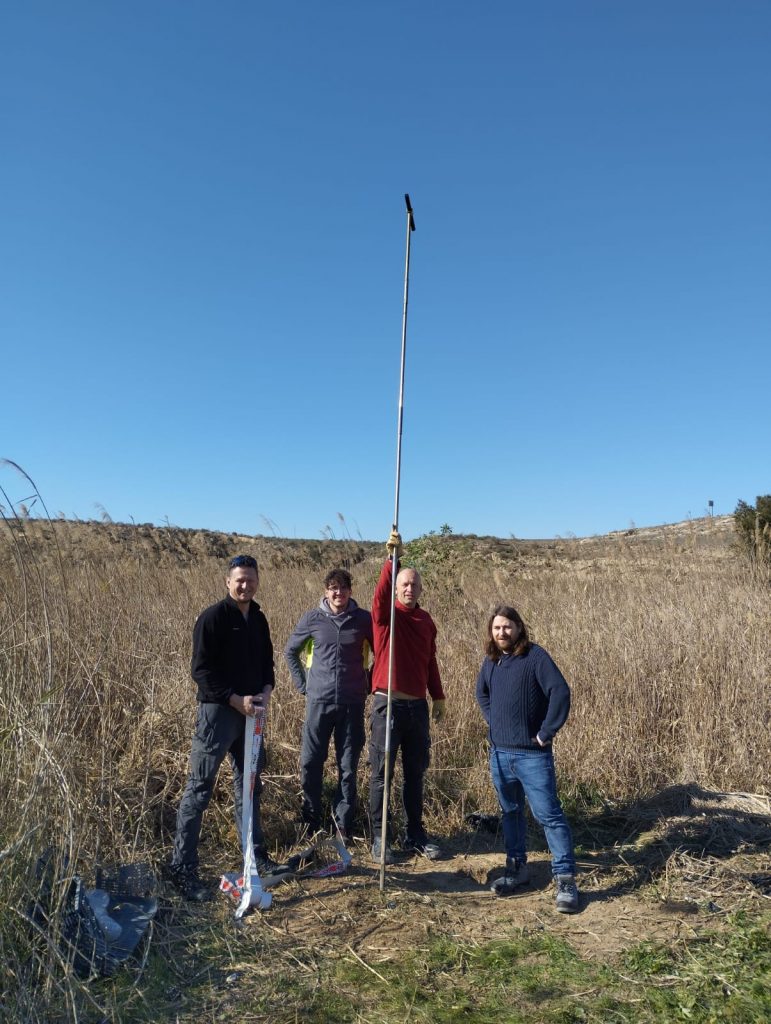



Rogério Portantiolo Manzolli (Universidad Autónoma Madrid), Claudi Blasco (Universidad Alicante), José Enrique Tent-Manclús (Universidad Alicante) and Carlos Arteaga Cardenau Universidad Autónoma Madrid) in Guardamar making a manual borehole.
Tags: MOLICO-CV
Recent Comments