The goal of this paper is the construction of computerized 3D visualization of geological structures. Several Python applications have been used to adapt the paper map-based geological classical information to numerical geological maps represented in HTML files. The models include a map with the stratigraphic and structural contacts and symbols, five serial vertical sections, and a geological block diagram, all with real topography. This block diagram made with 2D figures allows a 3D visualization. Palomeque area (Murcia region, southeastern Spain) has been used as a key-case. This area consists of a deformed Upper Cretaceous to Oligocene succession belonging to the Internal Zone Malaguide Complex. The main structure consists of two thrust-fold sheets forming an imbricate system, also affected by a set of strike-slip faults with a sinistral regime. The constructed maps show a good agreement with the published classical geological maps and cross-sections demonstrating the benefits of using these Python applications.
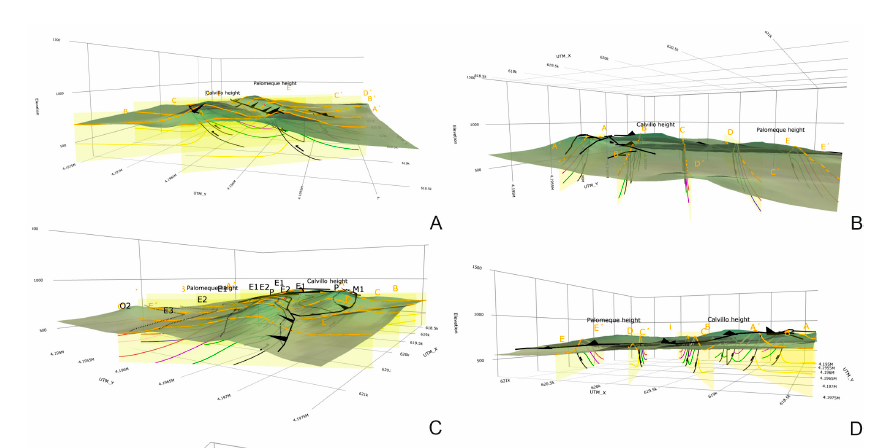
Cite as: Bullejos, M. and Martín-Martín, M. (2023): 3D Visualization of geological structures using Python: the case study of the Palomeque sheets (SE, Spain). Journal of Maps 19, NO. 1, 2282593 https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2023.2282593
Tags: 3d geological map, geological block diagram, Internal Betic Zone, Malaguide Complex, Python applications, thrust-fold sheets